E-E-A-T for AI 2026: Why ChatGPT Cites Authors with 'MD, PhD' 40% More Often
How Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness signals impact AI citations. Implementation guide with Schema.org examples and industry-specific credential strategies.
A doctor writes about heart disease. A blogger writes about heart disease. Which one does ChatGPT cite?
The answer isn't surprising, but the magnitude is: content from authors with visible credentials receives 40% more citations from AI models.
This guide explains how AI systems evaluate E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals, and provides actionable strategies to strengthen your authority for AI citations.
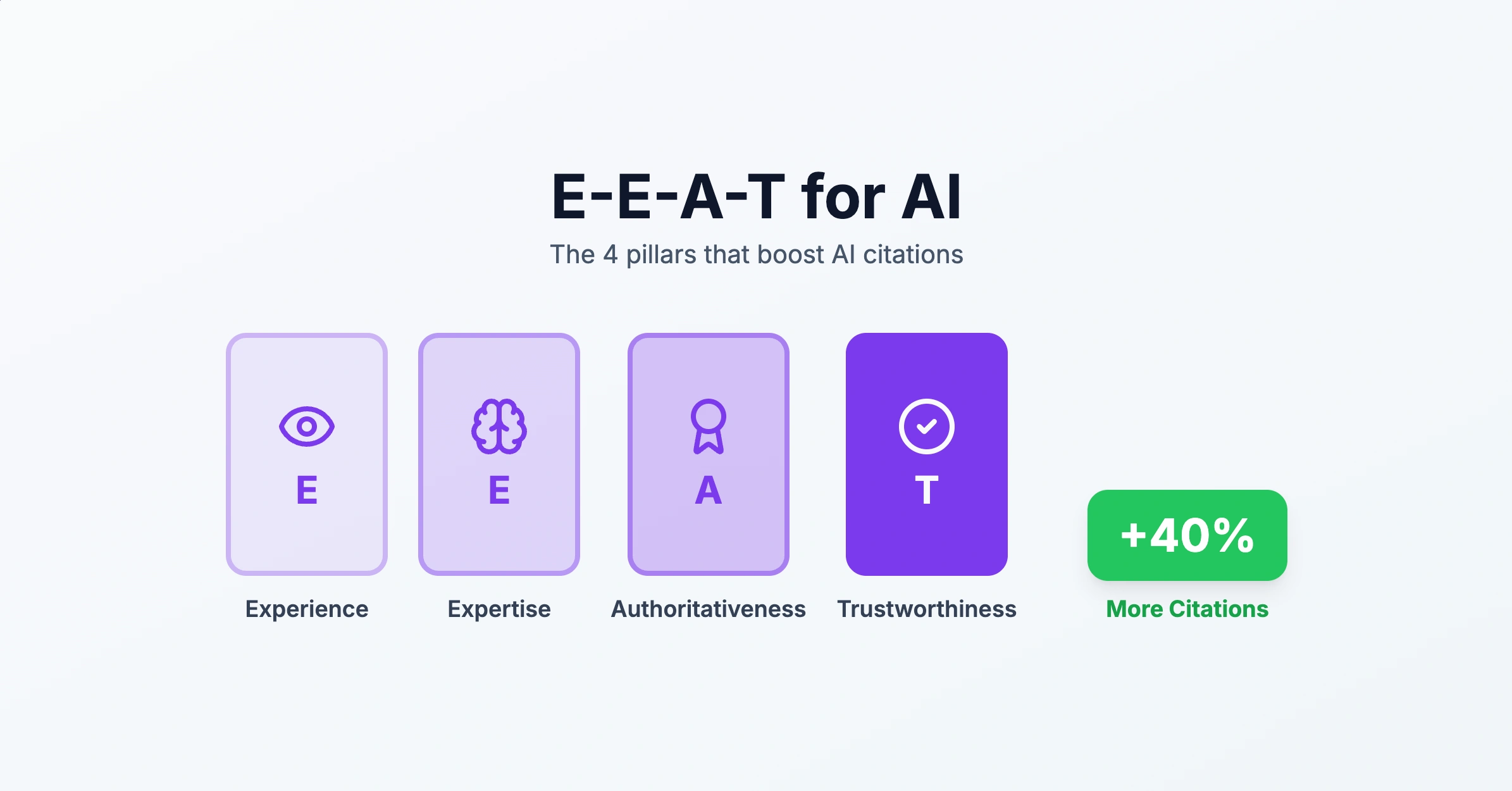
Understanding E-E-A-T in the AI Context
E-E-A-T originated as Google's quality evaluation framework, documented in their Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. While designed for human evaluators, these principles now influence how AI models select and prioritize sources.
The Four Pillars
| Pillar | Definition | AI Evaluation Signals |
|---|---|---|
Experience | First-hand knowledge of topic | Case studies, personal examples, methodology descriptions |
Expertise | Formal qualifications | Credentials, degrees, certifications, institutional affiliations |
Authoritativeness | Recognition by others | Citations by other sources, Wikipedia presence, awards |
Trustworthiness | Reliability and transparency | Source citations, conflict disclosure, accurate claims |
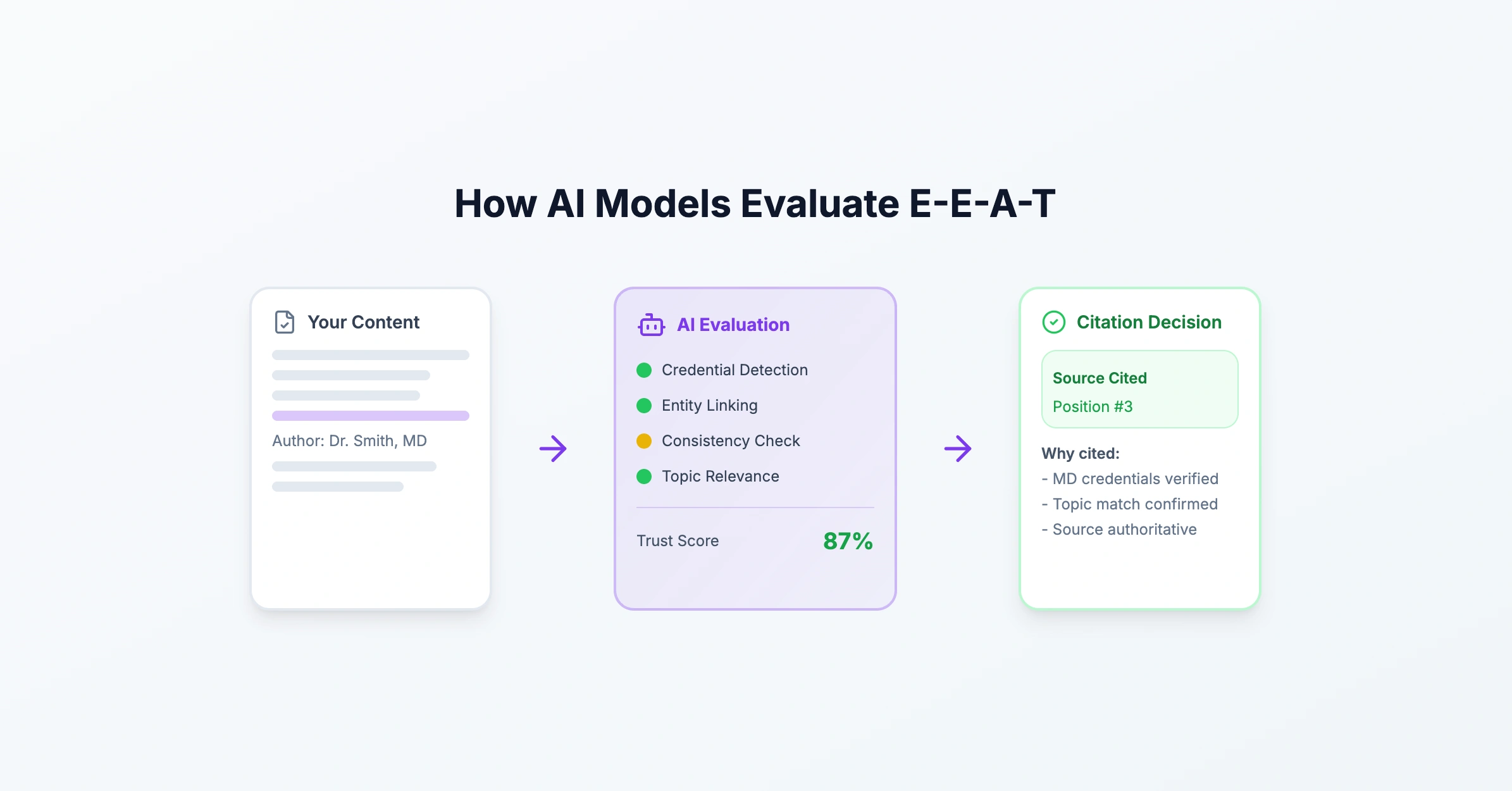
Why AI Models Care About E-E-A-T
AI models face a fundamental challenge: determining which sources to trust among millions of potential citations.
The solution: Use observable signals that correlate with reliability.
Princeton's GEO research demonstrates that AI visibility can increase up to 40% through content optimization. Credentials and authority signals are among the most impactful factors.
How models interpret credentials:
- Credential detection - Models identify patterns like "MD", "PhD", "CFA" in author information
- Entity linking - Cross-reference authors against Knowledge Graph entities
- Consistency verification - Check if credentials appear consistently across platforms
- Topic relevance - Evaluate whether credentials match the subject matter
Platform-Specific Authority Evaluation
Each AI platform weighs E-E-A-T signals differently:
| Platform | Primary Authority Signal | Secondary Signals |
|---|---|---|
ChatGPT | Formal credentials (MD, PhD) | Wikipedia presence, institutional affiliation |
Claude | Methodology transparency | Primary sources, limitation acknowledgment |
Perplexity | Freshness + credentials | Inline citations, comprehensive coverage |
Gemini | Google ecosystem (GBP, Knowledge Graph) | Reviews, NAP consistency |
→ Complete platform strategies: ChatGPT vs Perplexity vs Claude vs Gemini: Platform-Specific GEO Strategies
The rest of this guide focuses on how to build and implement E-E-A-T signals that work across all platforms.
Credentials That Matter by Industry
Not all credentials carry equal weight. Impact depends on topic relevance.

Healthcare and Medical
| Credential | Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
MD | Very High | Medical license required for clinical topics |
PhD | Very High | Research credibility |
RN, NP | High | Nursing and patient care |
PharmD | High | Medication topics |
Board certifications | High | Specialty authority |
Critical: Healthcare is a "Your Money Your Life" (YMYL) topic. AI models apply higher scrutiny. Credentials are nearly essential for citation consideration.
Finance and Business
| Credential | Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
CFA | Very High | Investment analysis |
CPA | Very High | Accounting and tax |
CFP | High | Personal finance |
MBA | Medium-High | General business strategy |
Series licenses | Medium | Securities and trading |
Context matters: An MBA writing about marketing strategy carries different weight than an MBA writing about tax code.
Legal
| Credential | Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
JD | Very High | Legal analysis |
Bar admission | Very High | State-specific advice |
LLM | High | Specialized legal areas |
Paralegal cert | Medium | Procedural content |
Warning: Legal content without credentials is rarely cited by AI for substantive legal questions.
Technology
| Credential | Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
CS/Engineering degrees | High | Technical architecture |
Patents | High | Innovation credibility |
Certifications (AWS, etc.) | Medium | Platform-specific expertise |
Open source contributions | Medium | Demonstrated technical skill |
Alternative path: In technology, demonstrated experience (GitHub profiles, technical blog posts, conference talks) can substitute for formal credentials more effectively than other industries.
Building Authority Without Formal Credentials
Not everyone has "MD" or "PhD" after their name. Here's how to build E-E-A-T through demonstrated expertise.
Experience-Based Authority
Show, don't just tell:
| Authority Signal | Example | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
Case studies | "We increased conversion 47% using this approach" | Detailed methodology and results |
Original research | "Survey of 500 marketers reveals..." | Primary data you collected |
Real examples | "Here's how Company X solved this" | Specific, named examples |
Track record | "Built 3 SaaS products to $1M ARR" | Verifiable achievements |
Platform Presence
Build consistent identity across platforms that AI models cross-reference:
| Platform | Purpose | Priority |
|---|---|---|
LinkedIn | Professional identity | Essential |
Personal website | Author page with bio | Essential |
Twitter/X | Industry engagement | High |
Industry publications | Bylined content | High |
Speaking/podcasts | Authority demonstration | Medium |
Consistency is critical: Same name spelling, same credentials, same affiliations across all platforms.
Is my brand visible in AI search?
Track your mentions across ChatGPT, Claude & Perplexity in real-time. Join 1,500+ brands already monitoring their AI presence with complete visibility.
Content-Based Authority
Establish expertise through content patterns:
- Comprehensive coverage - Be the definitive resource on specific topics
- Original insights - Provide perspective not available elsewhere
- Accurate citations - Reference primary sources correctly
- Regular updates - Maintain and improve content over time
- Community engagement - Respond to comments, answer questions
Technical Implementation: Schema.org for E-E-A-T
Person Schema (Author)
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Sarah Mitchell",
"honorificSuffix": "MBA, CFA",
"jobTitle": "VP of Product Strategy",
"description": "Product strategist with 12 years experience in B2B SaaS. Previously at Salesforce and HubSpot.",
"image": "https://example.com/authors/sarah-mitchell.jpg",
"url": "https://example.com/authors/sarah-mitchell",
"worksFor": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "TechCorp Inc",
"url": "https://techcorp.com"
},
"alumniOf": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Wharton School of Business"
},
"sameAs": [
"https://linkedin.com/in/sarahmitchell",
"https://twitter.com/sarahmitchell",
"https://techcorp.com/team/sarah-mitchell"
],
"knowsAbout": [
"Product Strategy",
"SaaS Metrics",
"Go-to-Market Strategy",
"B2B Marketing"
]
}
Article Schema with Author
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "SaaS Pricing Strategy: The Complete 2026 Guide",
"description": "Data-driven pricing strategies for SaaS companies...",
"datePublished": "2026-01-09",
"dateModified": "2026-01-09",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Sarah Mitchell",
"honorificSuffix": "MBA, CFA",
"url": "https://example.com/authors/sarah-mitchell"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Example Company",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://example.com/logo.png"
}
}
}
Organization Schema (Publisher)
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "TechCorp Inc",
"url": "https://techcorp.com",
"logo": "https://techcorp.com/logo.png",
"description": "Enterprise SaaS platform for...",
"foundingDate": "2018",
"numberOfEmployees": {
"@type": "QuantitativeValue",
"value": 250
},
"sameAs": [
"https://linkedin.com/company/techcorp",
"https://twitter.com/techcorp",
"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TechCorp"
],
"award": ["G2 Leader 2025", "Gartner Cool Vendor 2024"]
}
Building a Knowledge Graph Entity
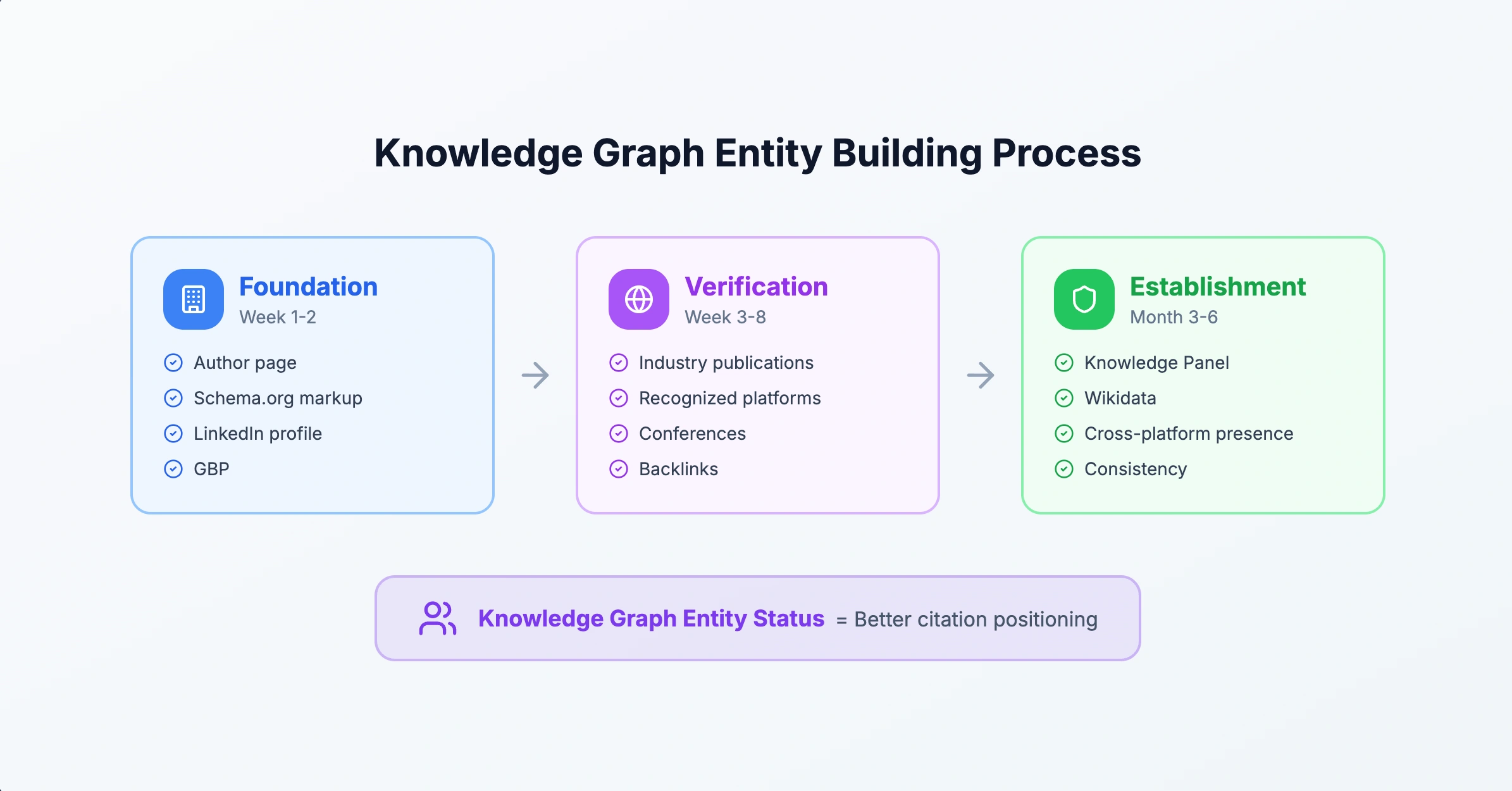
Getting recognized as a Knowledge Graph entity significantly improves AI citation positioning.
Requirements for Entity Status
| Requirement | What It Means | How to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
Notability | Notable enough for Wikipedia | Press coverage, awards, industry recognition |
Verifiability | Claims can be verified | Multiple independent sources confirming facts |
Consistency | Same information everywhere | Identical details across all platforms |
Structured data | Machine-readable identity | Schema.org on your site and author pages |
Entity Building Process
Phase 1: Foundation (Week 1-2)
- Create comprehensive author page on your site
- Implement Person Schema.org markup
- Optimize LinkedIn profile with same information
- Claim and verify Google Business Profile (if applicable)
Phase 2: Verification (Week 3-8)
- Get quoted in industry publications
- Publish on recognized platforms (Forbes, industry blogs)
- Speak at conferences or podcasts
- Build consistent backlinks to author page
Phase 3: Establishment (Month 3-6)
- Monitor for Knowledge Panel appearance
- Submit to Wikidata (if notability criteria met)
- Continue building cross-platform presence
- Maintain consistency across all platforms
Is my brand visible in AI search?
Track your mentions across ChatGPT, Claude & Perplexity in real-time. Join 1,500+ brands already monitoring their AI presence with complete visibility.
Wikipedia Considerations
Wikipedia presence correlates with early citation positioning (avg position 3.28 in our data). However:
What works:
- Adding yourself as a source to relevant articles (if genuinely contributing)
- Being mentioned in other Wikipedia articles
- Eventual standalone page if notability criteria met
What doesn't work:
- Creating your own Wikipedia page (conflict of interest)
- Promotional editing (will be removed)
- Exaggerating credentials or achievements
Realistic approach: Focus on becoming notable enough that others create your Wikipedia presence.
E-E-A-T Checklist
Immediate Implementation
- Add credentials to visible author bio on all content
- Implement Person Schema.org with
honorificSuffix - Ensure author page exists with comprehensive bio
- Verify LinkedIn matches website exactly
- Add
sameAslinks to all verified profiles
Content-Level Signals
- Include author byline on all articles
- Add "About the Author" section with credentials
- Cite primary sources (.gov, .edu, peer-reviewed)
- Acknowledge limitations and methodology
- Disclose any conflicts of interest
Platform Presence
- LinkedIn profile optimized and active
- Twitter/X professional and consistent
- Industry publication bylines (if possible)
- Speaker bio pages from conferences
- Institutional profile pages (employer, university)
Monitoring
- Search your name + credentials in quotes
- Check Google Knowledge Panel appearance
- Monitor brand mentions in AI responses
- Track citation positioning over time
📊 Monitor your AI brand mentions
Tracking how your E-E-A-T improvements affect AI citations requires consistent monitoring across platforms. Qwairy automatically tracks your brand mentions across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Gemini—showing you how authority signal changes impact real visibility over time.
Common E-E-A-T Mistakes
Mistake 1: Credential Inflation
The problem: Exaggerating or misrepresenting credentials.
Why it fails: AI models cross-reference information. Inconsistencies damage trust signals.
Example:
- ❌ "Harvard-educated" (attended 2-day executive program)
- ✅ "Harvard Business School Executive Education graduate"
Mistake 2: Ignoring Topic Relevance
The problem: Using credentials that don't match the topic.
Why it fails: An MD writing about software development doesn't get the same credential boost as writing about healthcare.
Instead: Emphasize credentials relevant to each piece of content.
Mistake 3: Schema.org Without Visible Signals
The problem: Adding structured data but not showing credentials on page.
Why it fails: Users can't see authority signals, and AI models may discount markup that doesn't match visible content.
Instead: Align Schema.org with prominent visible author information.
Mistake 4: Inconsistent Identity
The problem: Different names, titles, or credentials across platforms.
Why it fails: Entity verification requires consistency. "Dr. Sarah Chen" on LinkedIn but "S. Chen, PhD" on your website creates confusion.
Instead: Use identical formatting everywhere.
Key Takeaways
-
Credentials compound with content quality - MD/PhD credentials boost citations 40%, but only for relevant, high-quality content. Credentials without substance don't perform.
-
Platform preferences vary - ChatGPT values academic credentials, Claude prioritizes methodology, Perplexity rewards freshness, Gemini leverages Google ecosystem.
-
Experience can substitute for credentials - Demonstrated expertise through case studies, original research, and track record can build authority without formal qualifications.
-
Consistency enables verification - Same information across all platforms helps AI models verify and trust your identity.
-
Entity status improves positioning - Knowledge Graph recognition significantly improves where you appear in AI responses, even if citation volume comes from your specialized content.
-
E-E-A-T is ongoing - Building authority takes time. Focus on consistent, quality contributions rather than quick fixes.
Further Reading
- Google Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines
- Google's Article Schema Documentation
- Princeton GEO Research
- Complete AI Citation Optimization Guide
- 950K Citations Source Analysis
Measure how authority signals impact your visibility: Qwairy tracks your citation patterns across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Gemini. Monitor how credential updates, content improvements, and E-E-A-T enhancements translate to real citation changes—with historical trends and competitor comparisons.
Is Your Brand Visible in AI Search?
Track your mentions across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity and all major AI platforms. Join 1,500+ brands monitoring their AI presence in real-time.
Free trial • No credit card required • Complete platform access
Other Articles
How to Track AI Traffic in Google Analytics 4
Set up GA4 to measure visitors from ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude and other AI platforms. Includes referrer patterns, regex filters, and traffic quality analysis.
How to Find Relevant Prompts Using Google Search Console
Turn your GSC queries into AI visibility opportunities across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI Overview with practical regex patterns and a step-by-step workflow.